Addition and subtraction of angles
In trigonometry, addition and subtraction of angles describe the formulas that show how sine, cosine, and tangent change when two angles are added together or subtracted from each other.
The formulas make it possible to calculate values for new angles based on known ones.
For example, you can calculate cos(75°), even though it is not in the tables, by using cos(45° + 30°).
Formulas for addition and subtraction
Cosine:
$$ \large \cos(\alpha + \beta) = \cos(\alpha) \cdot \cos(\beta) - \sin(\alpha) \cdot \sin(\beta) $$
$$ \large \cos(\alpha - \beta) = \cos(\alpha) \cdot \cos(\beta) + \sin(\alpha) \cdot \sin(\beta) $$
Sine:
$$ \large \sin(\alpha + \beta) = \sin(\alpha) \cdot \cos(\beta) + \cos(\alpha) \cdot \sin(\beta) $$
$$ \large \sin(\alpha - \beta) = \sin(\alpha) \cdot \cos(\beta) - \cos(\alpha) \cdot \sin(\beta) $$
Tangent:
$$ \large \tan(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{\tan(\alpha) + \tan(\beta)}{1 - \tan(\alpha) \cdot \tan(\beta)} $$
$$ \large \tan(\alpha - \beta) = \frac{\tan(\alpha) - \tan(\beta)}{1 + \tan(\alpha) \cdot \tan(\beta)} $$
Example
We want to calculate \( \cos(75^\circ) \). It can be written as \( \cos(45^\circ + 30^\circ) \):
$$ \large \cos(75^\circ) = \cos(45^\circ + 30^\circ) $$
$$ \large = \cos(45^\circ) \cdot \cos(30^\circ) - \sin(45^\circ) \cdot \sin(30^\circ) $$
$$ \large = \tfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \cdot \tfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} - \tfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \cdot \tfrac{1}{2} $$
$$ \large = \tfrac{\sqrt{6}}{4} - \tfrac{\sqrt{2}}{4} = \tfrac{\sqrt{6} - \sqrt{2}}{4} $$
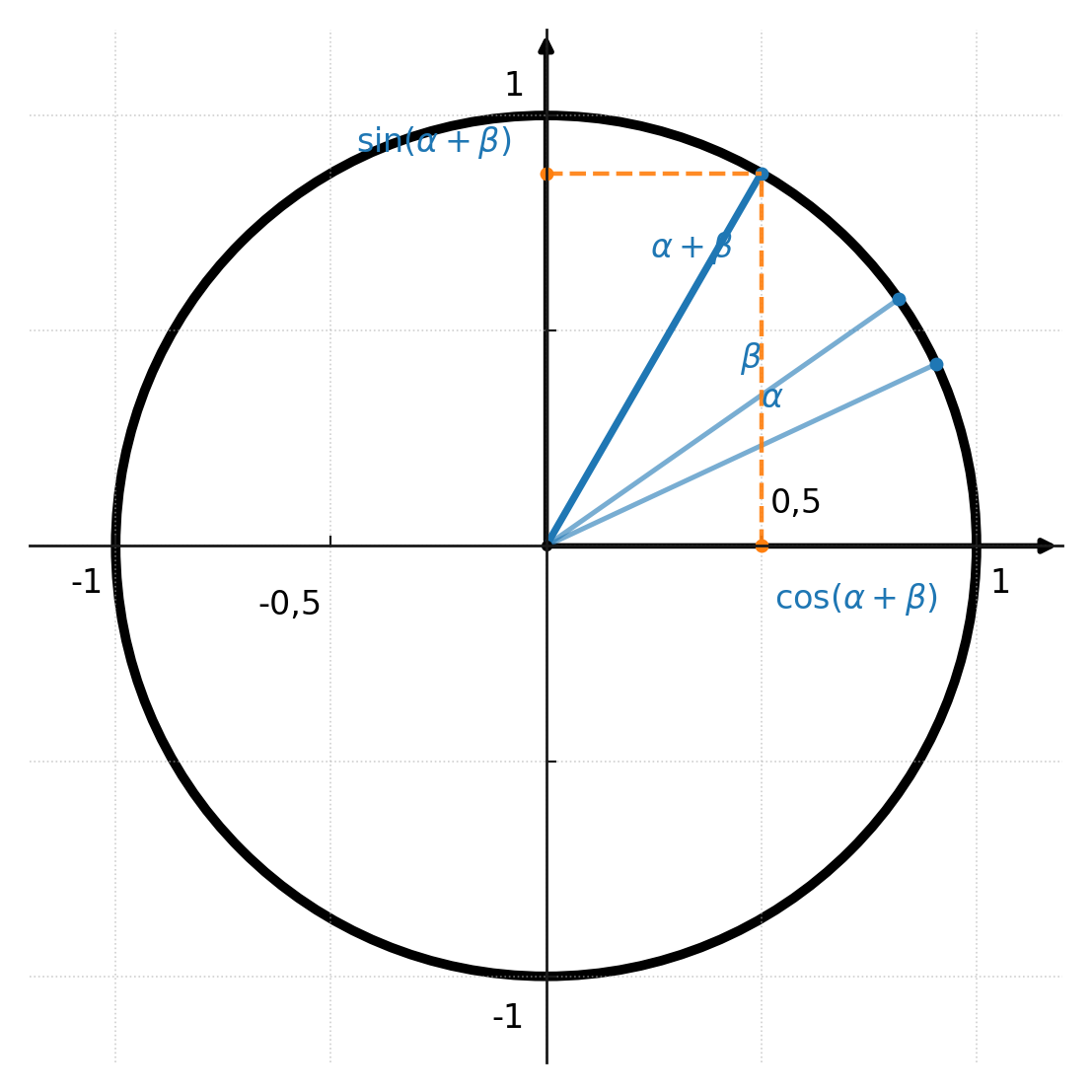
The formulas can also be understood geometrically from the unit circle.
Applications
- You can calculate exact values for angles such as 15°, 75°, and 105°.
- The formulas are the basis for double-angle and half-angle formulas (by setting \( \alpha = \beta \)).
- They are used in proofs and identities in advanced trigonometry and analysis.